Wireless is to use radio waves to transmit signals by changing the current in a conductor to generate radio waves, and then information can be loaded onto the radio waves for transmission.
In China, wireless frequency spectrum resources are state-owned natural resources, protected by the state, and can be used by people at the same time. Since the frequency spectrum is not restricted by region, airspace, or time domain, nor is it restricted by administrative regions or national boundaries, the development and utilization of these resources have strict international management regulations. Any department, region and individual, including any country, shall not be free to use the radio spectrum to avoid mutual interference. We should comprehensively adopt administrative, technical and other means to conduct consistent management of spectrum use internationally and within countries, and use spectrum resources scientifically and reasonably. Corresponding punishments should be made for the occupation of frequency spectrum resources, interference and damage to the facilities. Wireless management refers to the state’s unified planning and control of radio waves and satellite orbit resources. Internationally, radio management is mainly resolved by signing international agreements to uniformly allocate spectrum resources.
Spectrum monitoring, or wireless monitoring, is a technology for searching, measuring, analyzing, identifying, and locating wireless sources to obtain technical parameters, functions, categories, locations, and uses of wireless signals.
1. Main functions for spectrum monitoring
- Monitoring the electromagnetic environment, by monitoring the electromagnetic environment of the target area, allocate the required frequency bands reasonably.
- Observation of frequency and measurement of frequency channel occupancy, find and locate illegal radio monitoring, and ensure reasonable and smooth radio through strict monitoring;
- Identify the illegal source interference and stop its transmission. Regularly monitor whether the country’s electromagnetic radiation meets environmental requirements, control and manage existing legal radios, and maintain them to work in specific frequency bands, with the purpose of preventing radio interference.
2.Spectrum monitoring system composition
2.1 Monitoring system
The definition of spectrum monitoring is the analysis and statistics of various signal and noise parameters in the wireless frequency environment in a specific area using technical means such as monitoring, measurement, direction finding and positioning. The wireless monitoring system is composed of a number of fixed monitoring stations, semi-fixed monitoring stations, mobile monitoring stations, and control center unit. It mainly includes two systems. One is the monitoring system. The working components mainly include antenna feeders, receivers and software with diverse applications which can perform panoramic scanning at a high rate. The scanning frequency range is 30-3000MHz. It is the basic function of the wireless monitoring system to measure and monitor the frequency, power and bandwidth of the radio signal. The system can scientifically compare the monitored signal data with the data in the radio station teaching database and the data in the frequency database. Once illegal radio waves are found, they will be reported for processing. The monitoring system can accurately determine the signal distribution and background noise status in the entire frequency band, and display the monitoring results to the staff. The monitoring system can also set the detection threshold according to the actual situation, so as to carry out the measurement statistics of the utilization rate and channel occupancy of each service in an arbitrary time period, and provide full and accurate file for the development of wireless communication.
2.2 Radio direction-finding system
The radio direction-finding system is an important part of the wireless spectrum monitoring system, including several fixed direction finding stations, semi-fixed direction finding stations and mobile monitoring vehicles. The direction finding system will carry out direction finding work after networking. At present, in order to further improve the accuracy and scientificity of the data, the direction finding system is equipped with a high level of scientific and technological interference direction finder and spatial spectrum direction finder. At the same time, the direction finding system can calculate a reasonable probability area through multiple measurements and scientific convergence statistics, thereby improving the accuracy of the radio direction finding system. In addition, the direction-finding system can compare and modify the observation data with the data information of the relevant database, determine whether the transmitting station is legal, and improve the scientificity and accuracy of the direction-finding results.
3. Working principle and working mode of wireless spectrum monitoring
3.1 Working principle
Currently, the most widely used radio monitoring system mainly includes three modules, which are antenna feeder module, monitoring receiving module and monitoring software module. Spectrum monitoring is the core part of the radio monitoring system and working principle is relatively simple which mainly obtains various data required for radio monitoring by monitoring the cognitive radio environment, and can also strengthen the use of the spectrum system. Furthermore, the utilization rate of radio resources is improved, and the influence of the radio monitoring system when spectrum resources are scarce is controlled within a reasonable range. Spectrum technology can complete the intervention and application of cognitive users without affecting the normal use of users. It does not affect the normal use of users and can also complete accurate monitoring of idle spectrum resources. Radio spectrum monitoring technology has important applications in real life, and it is the most efficient and effective method among many monitoring methods.
3.2 Working mode
At present, in China the methods of wireless monitoring mainly includes daily routine monitoring, abnormal behavior monitoring, statistical measurement, mobile monitoring and related monitoring of interference signals. The main working methods of these types of radio monitoring have different workflows and characteristics. Among them, daily monitoring is mainly to collect reliable data and information, and scientifically and reasonably analyze and process the collected data and information, and reflect it in the form of graphs, tables, audio and video. The main task of abnormal monitoring is to monitor the monitoring stations and their working conditions, and compare the monitoring data with the standard data or the data under the normal working state of the equipment, and analyze the deviations, and report to the master station if the deviations exceed the standard range, and then correct the deviation in a reasonable and correct way.
The main method of monitoring frequency occupancy is statistical measurement. Through monitoring and reporting of frequency occupancy, it provides a reference for the adjustment of radio monitoring. The measurement of the interference signal correlation is mainly to monitor the interference source by comparing the correlation between different models and combine the actual feedback of the user to find the main signal by capturing the correct wave frequency. Mobile monitoring is mainly used to decentralize the monitoring of fixed monitoring stations. The transmission volume of mobile monitoring is very large, and there are also certain blind spots in its monitoring.
4. Main applications of spectrum monitoring antenna
The wireless spectrum is a finite resource used by many civil and military applications. To ensure proper and fair use, the spectrum is heavily regulated and frequency bands are allocated to specific users. The key to managing the spectrum is effective spectrum monitoring; monitoring who is using the spectrum, where and when they are using it and what they are using it for. Any breach of conditions can then be quickly spotted, and the spectrum utilized effectively.
The potential uses for a remote spectrum monitoring system are numerous, and each deployment can be flexibly configured to meet needs. Some examples of applications and use cases are:
- Interference hunting.
For satellite operators, monitor spectrum to insure area free of interference
- Infrastructure monitoring
Border patrol
Sea-Airport monitoring for interferenceStadium and eventmonitoringTracking illegal phones in correctional facilities
5. System equipment components
The regulator’s monitoring capabilities depend on three types of equipment: antennas, spectrum analyzers, and radio direction-finding equipment. Here we mainly introduce one of antenna types that using for spectrum monitoring purpose. Let us go ahead and take an Antesky spectrum monitoring antenna for an sample below.
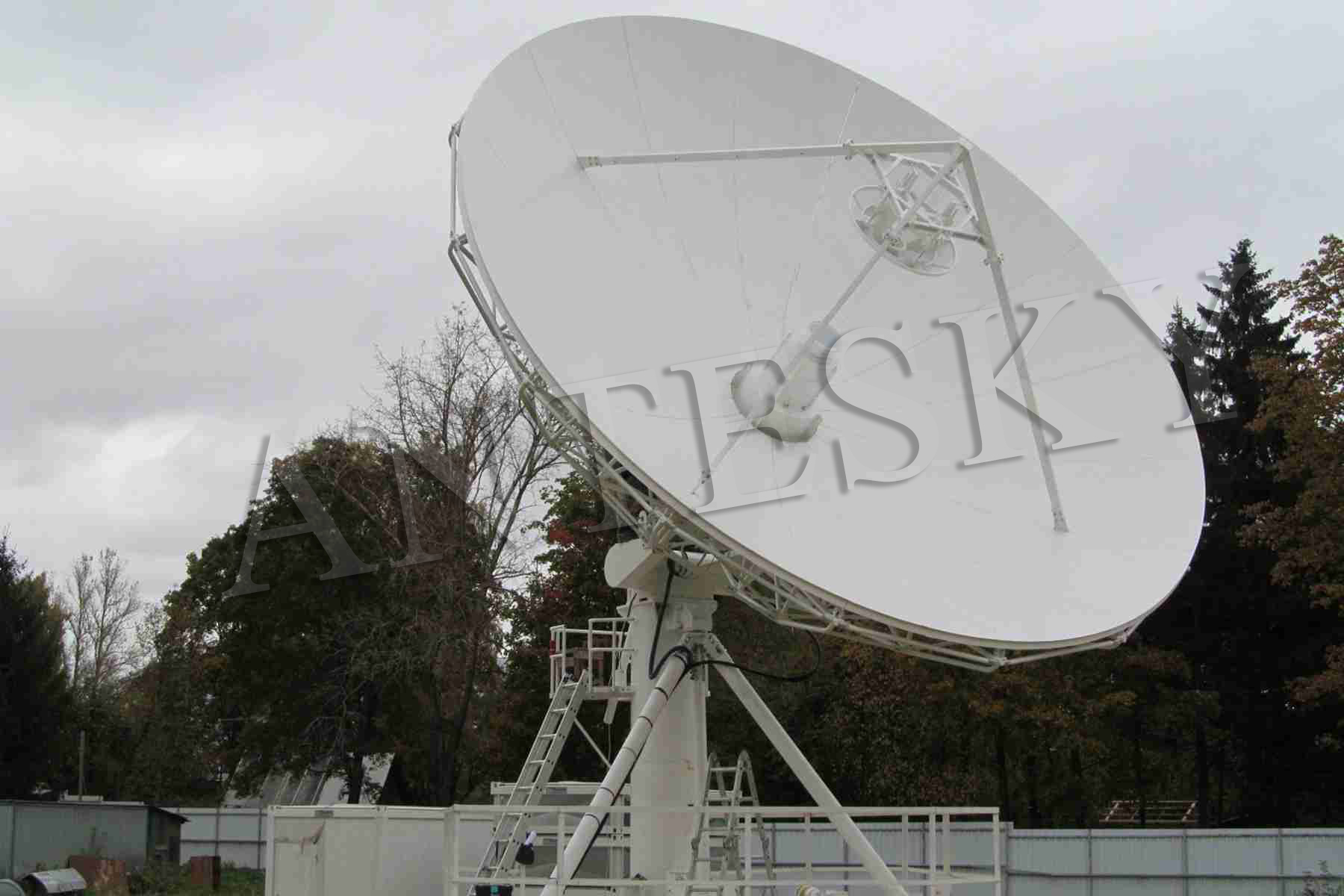
5.1 Antesky spectrum monitoring antennas
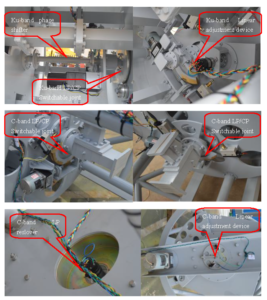
An antenna is simply an electronic component designed to radiate energy and transmit or receive radio waves. Different antenna types are used for different radio frequencies and for different coverage. All antennas radiate some energy in all directions but careful construction results in large directivity in certain directions and negligible power radiated in other directions. Antennas are linked to either radio receivers or signal generators of direction-finding equipment. As mentioned in the previous paragraph, different antenna types are needed for each application. Antesky had done various spectrum monitoring antenna projects before , which in 2015 for 9.0m C/Ku dual bands receive only antenna in Europe and in 2009 for 4 sets of 7.3m C/Ku dual bands receive only antenna
As an experienced and professional supploer for spectrum antenna, you do not need to worry about the parameter , installation details and shipping at all.
Also let us share with eletrical performance and feed network of spectrum monitoring antenna below for knowing more.
| Electrical performance | C-band | Ku-band |
| Frequency | 3.4~4.2GHz | 10.95~12.75GHz |
| Cross polarization isolation(At axis) | ≥30dB | ≥30dB |
| VSWR | ≤ 1.35 | ≤ 1.35 |
| Feed insertion loss | ≤ 0.35dB | ≤ 0.35dB |
| Circular axis ratio | ≤ 1.06 (0.5dB) | ≤ 1.06 (0.5dB) |
| Port isolation | ≥30dB (LP) | ≥27dB (CP) |
| Frequency isolation(C/Ku) | ≥30dB | |
| Pol. type | LP/CP (Motorized) | LP/CP (Motorized) |
| Feed port | 2 ports(RHCP/VLP,LHCP/HLP) | 2 ports(RHCP/VLP,LHCP/HLP) |
Diagram of spectrum monitoring antenna C&Ku feed network
Welcome to send us an inquiry via sales@antesky.com if you are interested in this item.
Further reading about 7.3m&9m C & Ku Band Cassegration Feed System Antenna
9.0M C and KU dual band Antenna Specification
7.3M C/KU Dual bands receive only antenna specification
9.0M C-band and Ku band Rx only antenna in Europe
7.3M C/KU switchable antenna in Europe
7.3m&9m C & Ku Band Cassegration Feed System Antenna