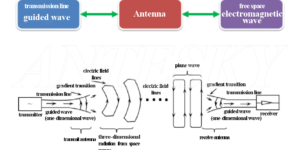
1. What is antenna?
The basic function of an antenna is energy conversion, which converts the electrical signal transmitted from the wire (feeder) into radio waves and transmits them into space. The mechanism of antenna radiation of electromagnetic waves is derived from Maxwell’s equations. Electric charges can generate electric fields, and currents can generate magnetic fields. Moreover, changing electric fields can generate changing magnetic fields, and changing magnetic fields can also generate changing electric fields. When the conductor carries alternating current, electromagnetic wave radiation will occur.
To put it simply, an antenna is a tool that converts electrical signals into electromagnetic wave signals.
2. Antenna parameter
2.1 Antenna gain value
Gain is an extremely important parameter of the antenna. It can measure the concentration of the antenna’s radiated energy. It refers to the ratio of the signal generated by the actual antenna and the ideal radiating unit at the same point in space under the same input power. Gain is closely related to the antenna pattern. The narrower the main lobe of the pattern and the smaller the side lobe, the greater the gain.
G=10lg(4πA/λ2)η
(G: antenna gain, unit dB; A: antenna aperture area, unit m2; D: antenna diameter, unit m; λ: operating wavelength, unit m; f: operating frequency, unit Hz; η: antenna power loss rate, generally 0.6~0.75)
It can also be seen from the formula that the gain of the antenna is proportional to the square of the antenna radius. The larger the antenna aperture, the higher the gain.
2.2 Antenna VSWR
Return loss calculation formula: Return loss = incident power / reflected power
When the feeder and antenna are conjugate matched, all energy is absorbed by the load, and there is only incident wave on the feeder, and no reflected wave.
When the antenna and feeder are not matched, that is, when the antenna input impedance is not equal to the feeder characteristic impedance, the load can only absorb part of the energy. Part of the energy of the incident wave is reflected back to form a reflected wave.
Antenna efficiency is generally defined as the ratio of the antenna’s radiated power to its input power. A high-efficiency antenna can radiate most of the input energy, while a low-efficiency antenna will have most of the energy absorbed as losses within the antenna or reflected back due to impedance mismatch.
2.3 Antenna Radiation pattern
The radiation pattern of an antenna is a function graph of the antenna’s radiation parameters (power flux density, field intensity amplitude and phase, polarization) changing with the spatial direction. The complete radiation pattern is a three-dimensional spatial graph.
Below is the onsite radiation patterns of Antesky 7.3m receive only antenna for reference.
2.4 Side Lobe Suppression (or side lobe level): Indicates the difference between the main lobe and the highest side lobe.
2.5 Horizontal Half-Power Beamwidth (HPBW): It refers to the range between the left and right angles where the main lobe drops 3dB from its maximum height, usually presented in two 2D radiation patterns: horizontal and vertical.
2.6 Antenna Noise temperature
Noise temperature is an important parameter for measuring the reception of weak signals. The noise entering the antenna mainly comes from the noise of the universe and the thermal noise from nature and the atmosphere. In the C band, the cosmic noise is very small, mainly the thermal noise of the earth and the atmosphere. In the Ku band, these noises also increase with the increase of frequency. The noise temperature is also related to factors such as the elevation angle, aperture, efficiency, accuracy, focal length/aperture ratio, etc. of the antenna. The smaller the elevation angle, the greater the thickness of the atmosphere through which the signal passes, so the stronger the meteorological noise and atmospheric noise, and the greater the noise temperature. The larger the aperture, the narrower the beam, and the smaller the noise temperature.
The ratio of the antenna gain to the antenna noise temperature is also called the quality factor (G/Ta). The larger the quality factor of the antenna, the greater the antenna gain, the smaller the noise temperature, and the better the performance of the antenna.
Detailed test result, please click this 7.3m receive only antenna testing.
2.7 Antenna polarization
In practical applications, electromagnetic waves are emitted by antennas, so the polarization of electromagnetic waves is also the polarization of antennas. Then corresponding to the three polarization modes of electromagnetic waves: linear polarization, circular polarization and elliptical polarization, antennas also have these three polarization types. Antenna polarization is an important factor in designing and erecting radio antennas and even integrating them into small wireless or mobile communication systems. Some antennas are vertically polarized, some are horizontally polarized, and some antenna types have different polarization forms.
3. The advantages of satellite communication over terrestrial communication are:
The coverage of satellites is much greater than that of terrestrial systems.
The transmission cost of satellites is independent of the distance to the center of the coverage area.
It is suitable for broadcasting, which facilitates rapid network expansion and emergency deployment of sites; satellite-to-satellite communication is very accurate.
The operating frequency is high, the bandwidth and communication capacity are large, and higher bandwidth is available.
4. The disadvantages of satellite communication:
It is expensive to launch satellites into orbit; “Europe and the United States quoted 100 million US dollars, and SPACE X quoted 60 million US dollars”
The satellite bandwidth is gradually running out; L, S, C, X, Ku, Ka, Q… frequency bands
The propagation delay in satellite communication is greater than that in terrestrial communication. When the signal transmitted from the earth station is forwarded to another earth station through the satellite, the one-way propagation time is about 0.27s. When two-way communication is carried out, the round-trip propagation delay is about 0.54s. Therefore, when making a call via satellite, you have to wait half a second to hear the other party’s reply after speaking, which makes people feel very uncomfortable;
The polar regions are communication blind spots, and the communication effect is poor in high-latitude areas;
There is a solar eclipse interruption phenomenon, which generally lasts for about 1 week during the spring and autumn equinoxes, lasting about 5-10 minutes each day, and occurs around noon;
Communication satellites have a certain lifespan, generally 15 years;
Antesky Science Technology Inc. was built in 1985, we’re mainly engaged in the design and manufacture of satellite communication large satellite dish,VSAT antenna,TVRO antenna, Portable flyaway antenna and relevant control and tracking system. We have a selected range of antenna in the frequency band, such as C-band, Ku-band, X-band, L-band, S-band, Ka-band, DBS-band.
If you are looking for any other satellite communication dish or related accessories, please send Antesky an inquiry via sales@antesky.com. Thanks!