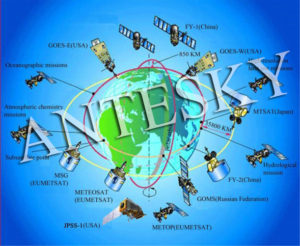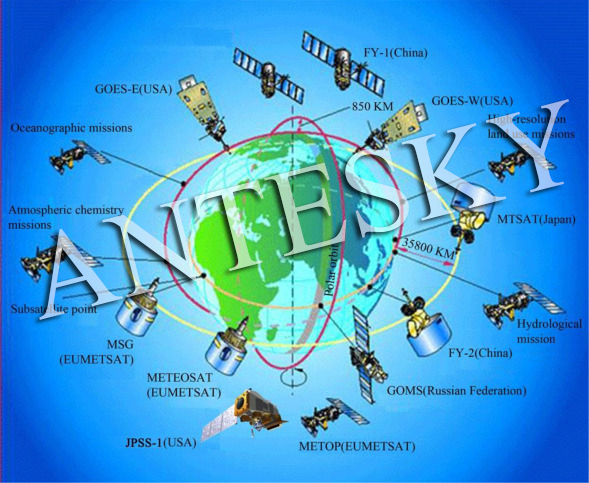
Meteorological satellites are artificial earth satellites that perform meteorological observations of the Earth and its atmosphere from space. The satellite carries a variety of meteorological remote sensors that receive and measure visible, infrared and microwave radiation from the Earth and its atmosphere and convert it into electrical signals for transmission to ground stations which restores the electrical signals from the satellites and maps them into various clouds, surface and sea pictures, and then further processes and calculates them to obtain various meteorological data.
1.The history of polar orbit meteorological satellite
According to different operational orbits, meteorological satellites are classified into geostationary satellites and polar-orbiting satellites.
1.1 The development of American polar orbit meteorological satellite
On April 1, 1960, the United States launched the first meteorological satellite “TIROS-1” (Tyros-1) television infrared observation satellite. From April 1, 1960 to July 2, 1965, a total of 10 were launched Tyros satellite.
US first-generation experimental operational meteorological satellite
From 1966 to 1969, the United States launched a total of nine TOROS operational meteorological satellites, named after the Environmental Survey Bureau (ESSA).
US second generation operational weather satellite
From 1970 to 1978, the United States launched a total of five meteorological satellites named after the United States Ocean and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) (including the improved Tyros satellites Ettos and NOAA-A~5).
US third-generation operational weather satellite
From 1978 to 1998, the United States launched a total of 10 new Tiros satellites (New Tiros) named TIROS-N and NOAA-6~NOAA-14.
US fourth-generation operational weather satellite
From 1998 to 2009, the United States launched a total of five advanced Tyros-N series satellites named NOAA-15~NOAA-19.
US fifth-generation operational weather satellite
The successful launch of the NPP satellite in 2011 marked the end of the era of the polar-orbiting meteorological satellite named NOAA in the United States and the beginning of a new generation of meteorological satellite era named after the NPP/JPSS (Joint Polar Orbiting Satellite System).
1.2 The development of Chinese polar orbit meteorological satellite
China’s first generation operational meteorological satellite
From May 10, 1999 to May 15, 2002, “FY-1C” and “FY-1D” were launched to form the first generation of operational satellites.
China’s third-generation operational meteorological satellite
On May 27, 2008, “FY-3A” was launched, and on November 5, 2010, “FY-3B” was launched.
1.3 The development of European polar orbit meteorological satellite
The European Meteorological Organization (EUMETSAT) polar orbit meteorological satellite started late but has a high starting point. In 2006, the European Meteorological Satellite Organization launched the first METOP-A of the first generation of business polar orbiting meteorological satellites, launched METOP-B in 2012 and METOP-C in 2017.
- The development of geostationary satellites
2.1 The development of American geostationary satellites
In 1966, NASA launched the first Geostationary Satellite-Application Technology Satellite (ATS-1) and subsequently launched two simultaneous orbiting meteorological satellites (SMS).
US first-generation operational geostationary meteorological satellite
From 1975 to 1978, the United States launched a total of four GOES-1~GOES-3 geostationary operational meteorological satellites.
US second-generation operational geostationary meteorological satellite
From 1980 to 1987, the United States launched a total of four GOES-4~GOES-7.
US third-generation operational geostationary meteorological satellite
From 1994 to 2001, the United States launched a total of five third-generation operational geostationary meteorological satellites of GOES-8~GOES-12.
US fourth-generation operational geostationary meteorological satellite
In 2006-2010, GOES-13~GOES-15 was the fourth generation of service geostationary satellites. In 2016, the satellite GOES-R was launched.
2.2 The development of European geostationary satellites
EUMETSA had launched the first geostationary satellite Meteosat-1 in 1977.
European first-generation operational geostationary meteorological satellite
From 1977 to 2001, the European Meteorological Satellite Organization launched and operated seven Meteosat-1 models.
European second-generation operational geostationary meteorological satellite
Three have been launched from 2002 to 2012, named Metrosat-8~Metrosat-10.
European third-generation operational geostationary meteorological satellite
2020 will launch the first satellite MTG.
2.3 The development of Chinese operational geostationary satellites
In 1986, China’s first geostationary meteorological satellite, Fengyun 2, was officially included in the national plan. The first one was launched on June 10, 1997, “FY-2A”. “FY-2B” was launched on June 25, 2000.
China’s first generation of operational geostationary meteor
From 2004 to 2012, China launched a total of four operational geostationary meteorological satellites FY-2C~FY-2F.
China’s second generation of operational geostationary meteor
Launched in 2015, “FY-4” consists of four satellites.
FY serial satellite is mostly use for meteorological application
2.4 The development of Japanese operational geostationary satellites
In 1977, the first operational geostationary meteorological satellite Himawari-1 was located at 140°E.
From 1977 to 1995, a total of five similar satellites were launched, collectively referred to as GMS-1~GMS-5.
Multi-function satellites (MTSAT-IR and MTSAT-2) were launched in 2005-2006.
Launched Himawari-8 in 2014.
2.5 The development of Indian operational geostationary meteorological satellites
India’s first generation of operational geostationary meteorological satellites
INSAT-1A~1D was launched from April 10, 1982 to June 12, 1990. In April 1982, the first INSAT-1A was launched, a total of four.
India’s second-generation operational geostationary meteorological satellites
INSAT-2A and 2B were launched by the Ariane-4 rocket (Ariane series rocket) on July 9, 1992 and July 22, 1993, by Ariane-4 on December 6, 1995 and June 3, 1997. The rocket fired INSAT-2C and 2D.
India’s third-generation operational geostationary meteorological satellites
INSAT-3A was launched by the Ariane-5 rocket on April 9, 2003, and INSAT-3B was launched by the Ariane-5 rocket on March 21, 2000. The INSAT-3C was issued by Ariane-4 on January 23, 2002. The rocket was launched. The INSAT-3E was launched by the Ariane-5 rocket on September 27, 2003. The INSAT-3DR was successfully launched by the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV Mk IIF05) on September 9, 2016.
Following is a map of Meteorological satellites around the world: