- LEO 500–2000km
The satellite in LEO orbits the earth fast. It will take only 90mins to orbit the earth – 45mins sunny side, 45mins dark side. Transmission delay and power consumption is small; satellite coverage area is small, and dozens of satellites can cover the whole world.
Satellites rise from the horizon to fall in a short time, so frequent switching between satellites is required. Therefore, the structure of the low-orbit system(LEO) is complicated, and difficult to operate, control, and manage.
Low-orbit satellites(LEO) are mainly used for taking pictures (as we usually call remote-sensing satellites). For example, for military target detection, low-orbit satellites(LEO) can easily obtain high-resolution images of targets. Low-orbit satellites(LEO) are also used for mobile-phone communications. Provide broadband services for terrestrial terminals.
The global internet penetration rate is about 51.7% by 2017, and half of the population does not have internet, so LEO market is vast.
Many high-tech companies (Boeing, Airbus, Amazon, Google, Facebook, SpaceX etc.) have launched large-scale low-orbit satellite system(LEO) solutions in order to seize limited low-orbit satellite orbits and spectrum resources, and strive to take the lead in the construction of low-orbit satellite communication system networking(LEO). Such as SpaceX’s Starlink plan is to reach a staggering number -12,000 satellites. In China, “Hongyan” and “Hongyun” low-orbit satellite communication(LEO) constellation plans will launch 300 and 156 low-orbit communication satellites respectively to form a space communication network. The two systems are planned to be completed by 2023.
- MEO 2000-20000km
MEO satellites combine the advantages of geostationary and low-orbiting earth satellites, enabling true global coverage and more efficient frequency reuse. MEO is mainly navigation applications. With an orbital height of 10,000 meters, a few satellites can cover the whole world, and a dozen can provide double coverage of most of the earth. In a certain sense, MEO system may be a superior solution for establishing global or regional satellite mobile satellite communication systems .
The representative MEO satellite Odyssey system is composed of 3 orbital planes with an inclination of 55 degree; the orbital height is 10354km; four satellites in each orbit.
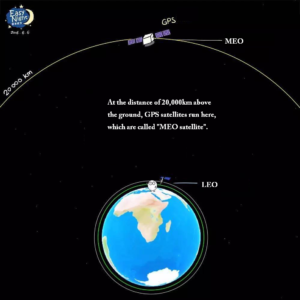
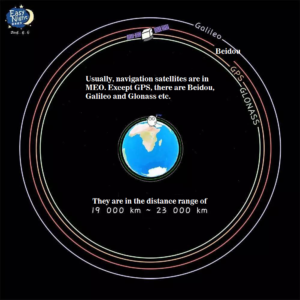
The GPS satellite orbit is about 20,000 kilometers – called a semi-synchronous orbit. It orbits the earth twice a day, that is 12 hours for one round. GPS arranges 6 orbital planes, each with 4-5 satellites. (There are 4 global navigation systems: US’s GPS, Russia’s Glonass, EU’s Calileo, China’s Beidou.)
- GEO 35800km
The geosynchronous orbit and the earth’s rotation period are the same.
Three satellites can cover the whole world. However, the disadvantages of synchronous satellites are: propagation delay and large link loss. (Severely affect the application of satellite mobile communications). It has high requirements for user terminals, and does not need to support mobile phones to communicate directly through satellites. It is necessary to use a satellite antenna (L-band) of bigger than 12 meters diameter. It is mainly used for VSAT system, TV broadcast signal forwarding, and less used for personal communication.
One of them is a special geosynchronous orbit, the geosynchronous stationary orbit. It is static viewing from the earth. (Fixed above the equator – The antegrade circular orbit is 35786 kilometers above the ground.) Except the period of operation cycle equals to the Earth’s rotation period, the eccentricity and inclination of the orbit are zero, and the satellite’s sub-satellite points trajectory position is always maintained invariably, satellites are stationary from any point on earth. (Note: The fixed antenna can always be aimed at the satellite, and the narrow beam antenna needs a tracking system.)